SR 11 – 7 Regulations
Introduction

AI in Banking Sector
1. Automated customer service:
2. Detecting fraudulent activity:
3. Financial forecasting:
4. Data Security:
What is Model Risk
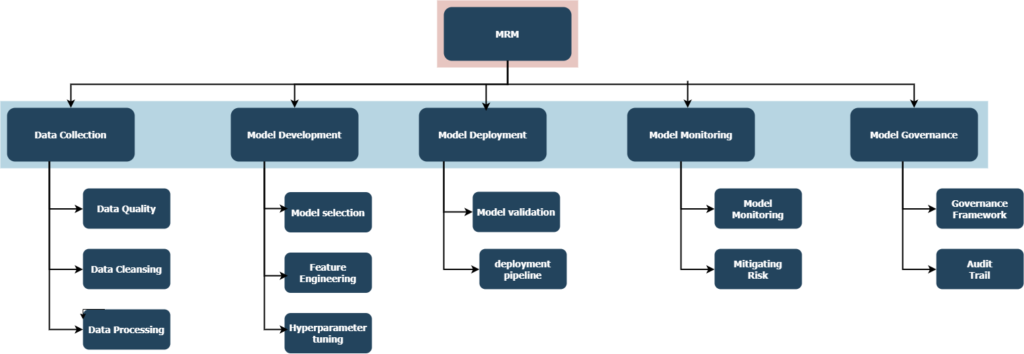
Model Risk Management (MRM)
Model Risk Management (MRM) in AI models is a process that involves identifying, assessing, and managing risks that could impact the accuracy or performance of a model. MRM is a subset of Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) that deals specifically with the risks associated with models.
MRM in AI models requires a combination of data science, ML engineering, and risk management practices to help organizations design and implement procedures to ensure the accuracy, robustness, and reliability of their data science models.
There are a number of ways to approach model risk management, but one common approach is to establish a model risk management framework. This framework should identify the key risks associated with AI models and establish processes for assessing and mitigating those risks.
To do this, organizations need to have a clear understanding of the potential risks associated with AI models and develop a framework that mitigates and manages the risks of the deployed models.
SR 11-7
SR 11-7 (Supervision and Regulatory Letter SR 11-7) guidance on MRM of AI models in the banking sector was released by the United States Federal Reserve and Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) in 2011 specific to the financing sector for algorithmic accountability act providing requirements for how a model should be developed, tested, validated and governed.
The guidelines are intended to help banks whenever to identify, assess, and manage risks due to inaccurate models, data quality issues, model complexity, or incorrect model implementation.
Guidelines
- A banking organization’s internal audit function should assess the overall effectiveness of the model risk management framework, including the framework’s ability to address both types of model risk for individual models and in the aggregate.
- Whenever a banking organization uses external resources for model risk management, the organization should specify the activities to be conducted in a clearly written and agreed-upon scope of work, and those activities should be conducted in accordance with SR11-7 protocols.
- All banking organizations should ensure that their internal policies and procedures are consistent with the risk management principles and supervisory expectations contained in this guidance
- Senior management is responsible for regularly reporting to the board on significant model risk, from individual models, and in the aggregate, and approving model risk management policies.
- These policies should also outline controls on the use of external resources for validation and compliance and specify how that work will be integrated into the model risk management framework.
- The role of the model owner involves ultimate accountability for model use and performance within the framework set by bank policies and procedures.
- The model owner should also ensure that models in use have undergone appropriate validation and approval processes, promptly identify new or changed models, and provide all necessary information for validation activities.
- Documentation and tracking of activities surrounding model development, implementation, use, and validation are needed to provide a record that makes compliance with policy transparent.
How to implement SR 11-7 in an organization
SR 11-7 implementation will vary depending on the specific AI models being used in the banking sector. However, some general tips on how to implement SR 11-7 for AI models in the banking sector include:
- Define your goals and objectives for a comprehensive risk management framework that includes policies, procedures, and processes to identify, assess, and manage risk.
- Work with regulatory bodies to establish an internal risk management committee composed of representatives from each functional area to ensure that AI models comply with all relevant regulations.
- To perform risk assessments for the purpose of evaluating risk management on a regular basis in order to identify any potential risks and processes to respond to those risks, and to report the information about those risks to appropriate stakeholders.
- Implement controls and safeguards to mitigate any risks and ensure that banks implement a risk management program throughout the organization with proper training for employees.
- To ensure that your AI models are operating as intended and that your risk management program remains current, you should monitor and evaluate them regularly
Dark
Light
Dark
Light

